链表数据结构详解:从单向链表到双向循环链表
链表的基本概念
链表是一种线性数据结构,由一系列节点组成,每个节点包含数据和指向下一个节点的指针。与数组不同,链表的内存空间不需要连续,这使得链表在动态内存分配方面更加灵活。
单向链表
单向链表是最简单的链表形式,每个节点只包含数据和指向下一个节点的指针。
节点定义
class ListNode {
constructor(val, next = null) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
基本操作实现
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.size = 0;
}
// 在链表头部插入节点
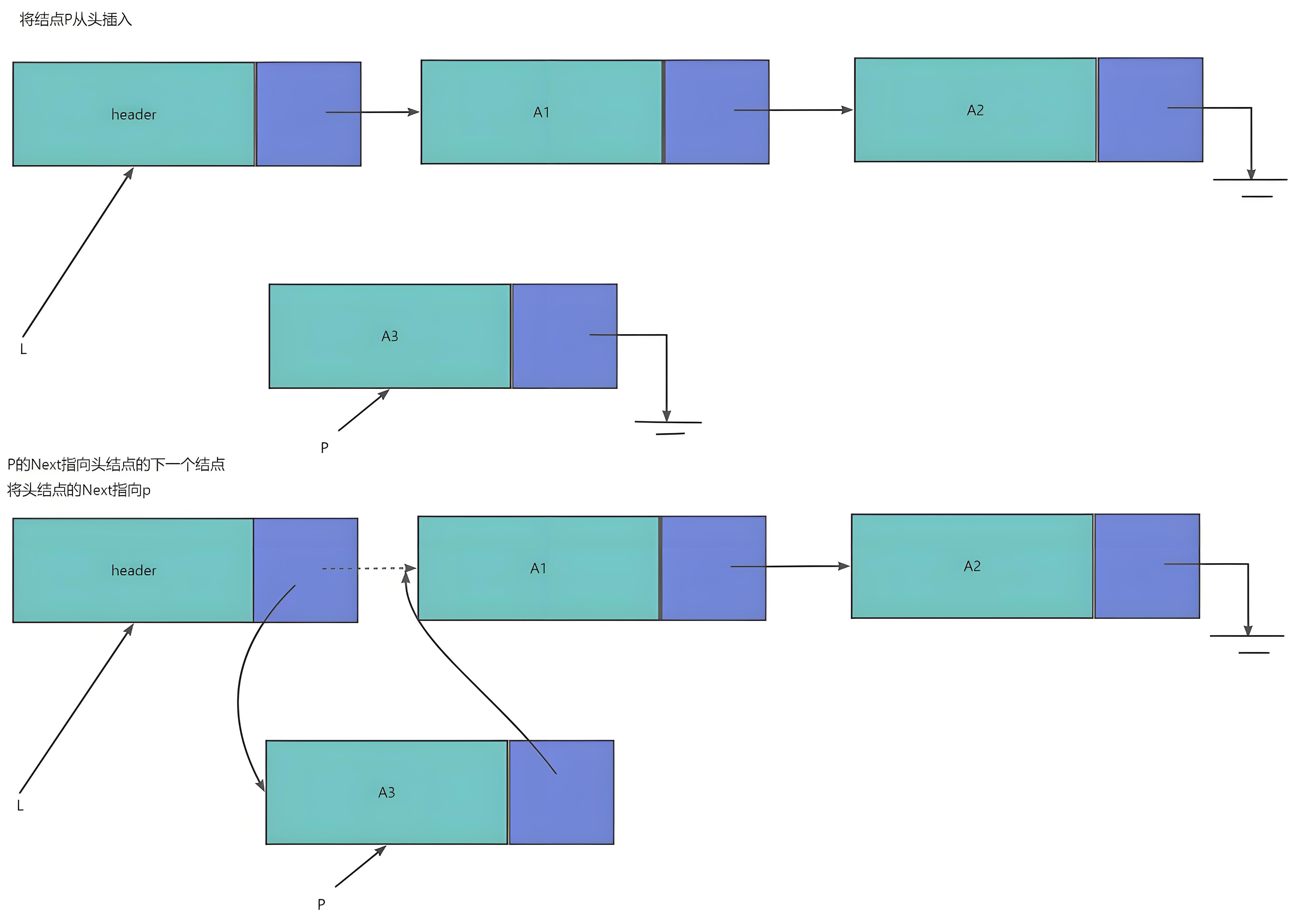
prepend(val) {
const newNode = new ListNode(val);
newNode.next = this.head;
this.head = newNode;
this.size++;
}
// 在链表尾部插入节点
append(val) {
const newNode = new ListNode(val);
if (!this.head) {
this.head = newNode;
} else {
let current = this.head;
while (current.next) {
current = current.next;
}
current.next = newNode;
}
this.size++;
}
// 删除指定值的节点
delete(val) {
if (!this.head) return false;
if (this.head.val === val) {
this.head = this.head.next;
this.size--;
return true;
}
let current = this.head;
while (current.next && current.next.val !== val) {
current = current.next;
}
if (current.next) {
current.next = current.next.next;
this.size--;
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 查找节点
find(val) {
let current = this.head;
while (current) {
if (current.val === val) {
return current;
}
current = current.next;
}
return null;
}
// 获取链表长度
getSize() {
return this.size;
}
// 打印链表
print() {
let current = this.head;
const result = [];
while (current) {
result.push(current.val);
current = current.next;
}
console.log(result.join(' -> '));
}
}
双向链表
双向链表每个节点包含指向前一个节点和后一个节点的指针,这使得双向链表可以向前和向后遍历。
class DoublyListNode {
constructor(val, prev = null, next = null) {
this.val = val;
this.prev = prev;
this.next = next;
}
}
class DoublyLinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.size = 0;
}
// 在头部插入
prepend(val) {
const newNode = new DoublyListNode(val);
if (!this.head) {
this.head = this.tail = newNode;
} else {
newNode.next = this.head;
this.head.prev = newNode;
this.head = newNode;
}
this.size++;
}
// 在尾部插入
append(val) {
const newNode = new DoublyListNode(val);
if (!this.tail) {
this.head = this.tail = newNode;
} else {
newNode.prev = this.tail;
this.tail.next = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
}
this.size++;
}
// 删除节点
delete(val) {
if (!this.head) return false;
let current = this.head;
while (current && current.val !== val) {
current = current.next;
}
if (!current) return false;
if (current.prev) {
current.prev.next = current.next;
} else {
this.head = current.next;
}
if (current.next) {
current.next.prev = current.prev;
} else {
this.tail = current.prev;
}
this.size--;
return true;
}
// 反向打印
printReverse() {
let current = this.tail;
const result = [];
while (current) {
result.push(current.val);
current = current.prev;
}
console.log(result.join(' <-> '));
}
}
循环链表
循环链表是链表的尾部节点指向头部节点,形成一个环形结构。循环链表可以是单向的也可以是双向的。
class CircularLinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.size = 0;
}
// 插入节点
insert(val) {
const newNode = new ListNode(val);
if (!this.head) {
this.head = newNode;
newNode.next = this.head; // 指向自己形成环
} else {
let current = this.head;
while (current.next !== this.head) {
current = current.next;
}
current.next = newNode;
newNode.next = this.head; // 新节点指向头节点
}
this.size++;
}
// 删除节点
delete(val) {
if (!this.head) return false;
let current = this.head;
let prev = null;
// 查找要删除的节点
while (current.val !== val) {
prev = current;
current = current.next;
if (current === this.head) {
return false; // 没有找到
}
}
// 删除节点
if (current === this.head) {
// 删除头节点
if (this.size === 1) {
this.head = null;
} else {
let tail = this.head;
while (tail.next !== this.head) {
tail = tail.next;
}
this.head = this.head.next;
tail.next = this.head;
}
} else {
prev.next = current.next;
}
this.size--;
return true;
}
}
经典算法问题
反转链表
function reverseList(head) {
let prev = null;
let current = head;
while (current) {
const next = current.next;
current.next = prev;
prev = current;
current = next;
}
return prev;
}
// 递归版本
function reverseListRecursive(head) {
if (!head || !head.next) {
return head;
}
const newHead = reverseListRecursive(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return newHead;
}
检测环
// 使用快慢指针检测环
function hasCycle(head) {
if (!head || !head.next) return false;
let slow = head;
let fast = head.next;
while (fast && fast.next) {
if (slow === fast) return true;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return false;
}
// 找到环的起始位置
function detectCycle(head) {
if (!head || !head.next) return null;
let slow = head;
let fast = head;
// 第一阶段:检测是否有环
while (fast && fast.next) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow === fast) break;
}
if (slow !== fast) return null; // 没有环
// 第二阶段:找到环的起始位置
slow = head;
while (slow !== fast) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
合并两个有序链表
function mergeTwoLists(l1, l2) {
const dummy = new ListNode(0);
let current = dummy;
while (l1 && l2) {
if (l1.val <= l2.val) {
current.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
current.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
current = current.next;
}
// 连接剩余节点
current.next = l1 || l2;
return dummy.next;
}
链表与数组的对比
| 操作 | 数组 | 链表 |
|---|---|---|
| 随机访问 | O(1) | O(n) |
| 插入/删除(已知位置) | O(n) | O(1) |
| 插入/删除(头部) | O(n) | O(1) |
| 内存使用 | 连续 | 分散 |
| 缓存友好性 | 好 | 差 |
实际应用场景
- LRU缓存:使用双向链表实现最近最少使用算法
- 音乐播放器:实现播放列表的循环播放
- 撤销操作:使用栈(基于链表)实现撤销功能
- 哈希表冲突解决:使用链表处理哈希冲突
- 操作系统:进程调度、内存管理等
LRU缓存实现示例
class LRUCache {
constructor(capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
this.cache = new Map();
this.head = new DoublyListNode(0);
this.tail = new DoublyListNode(0);
this.head.next = this.tail;
this.tail.prev = this.head;
}
get(key) {
if (this.cache.has(key)) {
const node = this.cache.get(key);
this.moveToHead(node);
return node.val;
}
return -1;
}
put(key, value) {
if (this.cache.has(key)) {
const node = this.cache.get(key);
node.val = value;
this.moveToHead(node);
} else {
const newNode = new DoublyListNode(value);
newNode.key = key;
if (this.cache.size >= this.capacity) {
const tail = this.removeTail();
this.cache.delete(tail.key);
}
this.addToHead(newNode);
this.cache.set(key, newNode);
}
}
addToHead(node) {
node.prev = this.head;
node.next = this.head.next;
this.head.next.prev = node;
this.head.next = node;
}
removeNode(node) {
node.prev.next = node.next;
node.next.prev = node.prev;
}
moveToHead(node) {
this.removeNode(node);
this.addToHead(node);
}
removeTail() {
const lastNode = this.tail.prev;
this.removeNode(lastNode);
return lastNode;
}
}
总结
链表是一种重要的数据结构,虽然在某些操作上不如数组高效,但在动态内存分配和频繁插入删除的场景下具有独特优势。掌握链表的各种变体和经典算法,对于解决复杂的数据结构问题具有重要意义。
在实际开发中,要根据具体需求选择合适的数据结构。链表特别适合实现栈、队列、LRU缓存等需要频繁插入删除操作的场景。
评论区